2010년 11월 29일 월요일
Practice the Zen principle of Beginner's Mind
In order to succeed in Anthropologist role, people should set aside what they “know”. They have to have the wisdom to observe with a truly open mind. But seeing with fresh eyes may be the one of the hardest parts of the innovation process.Picking up on the smallest nuances of your customers can offer tremendous opportunities, so in order to be equipped to this, Tom Kelly suggested to practice the Zen principle of “Beginner's Mind,” so set aside all the preconception and have a wisdom to observe with a truly open mind.From Ten faces of innovation written by Tom Kelley, GM of IDEO.
Techmining 을 아세요?
코골이 침대의 발명은 국방에서 연구되는 기술을 응용한 것이다. 코를 골기 시작하면 침대의 상단부분이 위로 올라가서 잠자는 사람의 머리를 올려서 코고는 것을 방지한다는 것이다. 이 기술은 원래 국방에서 연구되던 것인데 스웨덴 궤텐버그대학과 디자인회사가 고안해냈다고 한다. 침대에 센서가 컴퓨터로 연결되어있어, 심장박동, 호흡리듬, 수면자의 움직임과 코고는 소리등을 모니터하여 한다고 한다. 전문가들은 코고는 사람의 머리를 들어줌으로써 목구멍 뒤로 혀가 빠지는 것을 방지하여 코고는 것을 멈추게 한다고 한다. 코고는 것이 멈추면 다시 원래 위치로 침대를 되돌려 준다. 이와관련된 재밌는 광고도 보세요. 이러한 다른 산업이나 지역에서 best practice 를 탐색하는 것은 많은 성공적 기업이 이미 실행하고 있다. 특히 제품을 개발할때 소위 fuzzy front-end 즉 ideation 이나 concept design 단계에서 신기술의 동향분석 혹은 특허정보검색등을 통해 외부의 아이디어를 탐색하는 이른바, techmining 의 분야가 점점 더 실생활에 널리 사용됨을 느낀다.
오늘 CIOBIZ 에서 이와 관련한 기사를 발견했다.
기업의 정보 서비스 체계가 빠르게 변화하고 있다. 기존 정형 데이터 중심의 정보 활용 체계로는 한계가 있다고 판단, 시맨틱, 오피니언 마이닝, 토픽 맵, 소셜네트워크분석(SNA) 등을 기반으로한 다양한 차세대 정보 서비스를 검토하고 있는 것이다.29일 투이컨설팅 이승범 수석은 “기업이 제공하는 정보가 스팸화되고 있고, 정보의 불신감으로 인한 부가가치 창출 효과가 지속적으로 감소하고 있는 실정”이라며 “이에 기업들이 기업 업무 활동의 효용성을 증대시킬 수 있는 새로운 정보 체계 구현에 나서고 있다”며 기업들의 차세대 정보 서비스 도입 배경에 대해 이같이 설명했다.현재 시장에서 차세대 정보 서비스로 두각을 나타내고 있는 것은 시맨틱 검색 서비스와 SNA 등이 대표적이다. 시맨틱 검색 서비스는 검색어에 대한 정보 사용자의 의도나 의미를 분석해 검색 결과를 가공해 제공하는 서비스를 말한다. 이미 국내에 소개된 지는 오래됐지만 그동안 성능 등의 문제로 도입을 꺼려왔다. 하지만 기술적인 성장과 함께 시장 인식 변화에 따라 시맨틱 검색 서비스가 빠르게 기업내 정보 서비스 시장에 흡수되고 있다.삼성전자 마케팅팀에서는 각종 논문, 학술지, 기술문서 등을 모두 통합해 신기술에 대한 트렌드 분석 등의 작업에 적용하고 있다. 빌보드 차트처럼 순위별로 분석 결과치가 나오면 뜨는 기술과 지는 기술, 정체돼 있는 기술 등이 무엇인지를 분석할 수 있다.이승범 수석은 “문서의 웹에서 데이터의 웹으로 전화하는 과정에서 차세대 정보 서비스로서 가장 커다란 가능성을 보여주고 있는 것이 바로 시맨틱 검색”이라며 “이는 대용량 정보처리기술, 온톨로지 모델링, 텍스트 마이닝 등 다양한 관련 기술들과 융합돼야 그 진가를 발휘할 수 있다”고 설명했다.
SNA는 국내에서 이미 수사 정보 서비스에 활용되고 있다. 범죄 조직 구성원들의 전화 기록을 SNA 기업으로 재구성해서 추가적인 범죄 용의자에 대한 정보를 추론해 내는 것이다. 통일부에서는 북한의 정세나 동향 분석 등에 활용하고 있다. 기업에서는 주로 인맥관계 분석이나 특정 이슈에 대한 연관 분석 등에 사용하고 있다.또한 기업들이 고객관계관리(CRM) 시스템을 통해 고객이 진정으로 원하는 서비스와 가치를 식별하기 어려워짐에 따라 특정 상품에 대한 고객 반응을 추출해 전반적인 평가를 도출하는 오피니언 마이닝 기반 정보 서비스도 주목받고 있다. 이는 텍스트를 분석해 특정 키워드간의 연계성을 추출하고 그 연계성에 근거해 정보를 도출하는 원리다.오피니언 마이닝 기반 정보 서비스는 한국전력 등에서 민원 서비스 조사에 사용하고 있다. 민원인들의 반응을 추출해 민원 유형을 분류하고, 민원 제기 원인을 파악해 민원 서비스 개선에 적극 활용하는 것이다.이 외에 차세대 정보 서비스로 패턴 기반정보 서비스도 보험, 통신, 카드 등의 산업군에 일부 적용되고 있다. 이는 기존에 나타난 패턴 외에 신규 패턴에 대한 분석이나 미래 패턴에 대한 예측 등을 기반으로 제공하는 서비스로, 주로 국내에서는 금융권에서 사기 의심자를 조사하는 데 쓰이고 있다. 삼성생명은 패턴 기반 분석 서비스를 도입해 보험사기 분석 작업에 활용하고 있다.
오늘 CIOBIZ 에서 이와 관련한 기사를 발견했다.
기업의 정보 서비스 체계가 빠르게 변화하고 있다. 기존 정형 데이터 중심의 정보 활용 체계로는 한계가 있다고 판단, 시맨틱, 오피니언 마이닝, 토픽 맵, 소셜네트워크분석(SNA) 등을 기반으로한 다양한 차세대 정보 서비스를 검토하고 있는 것이다.29일 투이컨설팅 이승범 수석은 “기업이 제공하는 정보가 스팸화되고 있고, 정보의 불신감으로 인한 부가가치 창출 효과가 지속적으로 감소하고 있는 실정”이라며 “이에 기업들이 기업 업무 활동의 효용성을 증대시킬 수 있는 새로운 정보 체계 구현에 나서고 있다”며 기업들의 차세대 정보 서비스 도입 배경에 대해 이같이 설명했다.현재 시장에서 차세대 정보 서비스로 두각을 나타내고 있는 것은 시맨틱 검색 서비스와 SNA 등이 대표적이다. 시맨틱 검색 서비스는 검색어에 대한 정보 사용자의 의도나 의미를 분석해 검색 결과를 가공해 제공하는 서비스를 말한다. 이미 국내에 소개된 지는 오래됐지만 그동안 성능 등의 문제로 도입을 꺼려왔다. 하지만 기술적인 성장과 함께 시장 인식 변화에 따라 시맨틱 검색 서비스가 빠르게 기업내 정보 서비스 시장에 흡수되고 있다.삼성전자 마케팅팀에서는 각종 논문, 학술지, 기술문서 등을 모두 통합해 신기술에 대한 트렌드 분석 등의 작업에 적용하고 있다. 빌보드 차트처럼 순위별로 분석 결과치가 나오면 뜨는 기술과 지는 기술, 정체돼 있는 기술 등이 무엇인지를 분석할 수 있다.이승범 수석은 “문서의 웹에서 데이터의 웹으로 전화하는 과정에서 차세대 정보 서비스로서 가장 커다란 가능성을 보여주고 있는 것이 바로 시맨틱 검색”이라며 “이는 대용량 정보처리기술, 온톨로지 모델링, 텍스트 마이닝 등 다양한 관련 기술들과 융합돼야 그 진가를 발휘할 수 있다”고 설명했다.
SNA는 국내에서 이미 수사 정보 서비스에 활용되고 있다. 범죄 조직 구성원들의 전화 기록을 SNA 기업으로 재구성해서 추가적인 범죄 용의자에 대한 정보를 추론해 내는 것이다. 통일부에서는 북한의 정세나 동향 분석 등에 활용하고 있다. 기업에서는 주로 인맥관계 분석이나 특정 이슈에 대한 연관 분석 등에 사용하고 있다.또한 기업들이 고객관계관리(CRM) 시스템을 통해 고객이 진정으로 원하는 서비스와 가치를 식별하기 어려워짐에 따라 특정 상품에 대한 고객 반응을 추출해 전반적인 평가를 도출하는 오피니언 마이닝 기반 정보 서비스도 주목받고 있다. 이는 텍스트를 분석해 특정 키워드간의 연계성을 추출하고 그 연계성에 근거해 정보를 도출하는 원리다.오피니언 마이닝 기반 정보 서비스는 한국전력 등에서 민원 서비스 조사에 사용하고 있다. 민원인들의 반응을 추출해 민원 유형을 분류하고, 민원 제기 원인을 파악해 민원 서비스 개선에 적극 활용하는 것이다.이 외에 차세대 정보 서비스로 패턴 기반정보 서비스도 보험, 통신, 카드 등의 산업군에 일부 적용되고 있다. 이는 기존에 나타난 패턴 외에 신규 패턴에 대한 분석이나 미래 패턴에 대한 예측 등을 기반으로 제공하는 서비스로, 주로 국내에서는 금융권에서 사기 의심자를 조사하는 데 쓰이고 있다. 삼성생명은 패턴 기반 분석 서비스를 도입해 보험사기 분석 작업에 활용하고 있다.
구글은 마이크로소프트처럼 처할 위험에 있는가?
Techcrunch 에서 Peter Sims 라는 저자가 JP Morgan 의 "thought leader dinner"에 초대되어 테이블에 앉은 사람들과 장수기업과 단명할 가능성이 있는 기업을 뽑다가, 15명중 12명이 구글을 단명할 기업 판별했다는 재밌는 기사가 있군요. 다음은 기사의 일부 입니다....놀라웠다. 그러나 그 방에 있었던 의견은 과거 성적에 관한 것이 아니라 구글의 미래에 관한 통찰력에서 나온 것이었다. 아래는 단명에 이르는 이유들이다.
1. 구글은 과거 수년간 심각한 인재 유출을 겪었다.구글의 근속률은 높은 편이지만, 구글의 인재 문제는 수가 아니라 누가 나가며 왜 나가냐의 유형의 문제다. 구글의 인재 유출은 여기를 참조. Facebook 과 Zynga 는 실리콘벨리에서 가장 선호되는 직장으로 여겨지는데, 구글에서는 특히 중요시되는 모바일 관련 안드로이드 프로덕트 매니저인 Erick Tseng 과 같은 이가 Facebook 으로 줄줄이 떠나는 것을 보아왔다.구글 내부 소식에 가까운 이에 따르면, 구글 상부에 회사 초기의 혁신적 문화을 이끌던 관리자들이 천천히 교체되고 있다. 한정되어 있다고 느끼고 동기부여가 되지않는 기업가 타입과 석학들이 움직인다. 사람들은 심지어 2004-2005년간에 야후가 더이상 그들이 입사했던 이전의 실력주의가 통용되지 않아 사람들이 떠났던 일을 회상하게 한다고까지들 했다.
2. 회사는 이제 손쉽게 성장할 수 있는 기회가 바닥나고 큰 규모의 새로운 매출을 찾아야 한다.검색시장이 성장 한계에 다다른 만큼, "큰 투자"에 점점 더 필요성을 느낀다. 이것이 성숙단계에 접어든 회사의 CEO 가 "큰 숫자의 폭정"을 야기하는 문제다. 작은 기반에서 인상적으로 성장한 모바일 검색이 있지만, 회사의 근본적 차이를 만들기에는 아직 너무 작다. 회사는 분명히 미친듯이 모바일과는 다른 성장 동력을 찾으려 시도한다. 최근 7000억원 규모의 ITA 인수가 중간에서 대규모의 투자를 어떻게 전개할 것인가의 관점에서 좋은 사례가 된다. 이는 성장율을 유지하게 위해 점점 더 큰 부분의 매출을 찾아야 함이다. 이러한 문제는 혁신을 연구하는 학자인 Clayton Christensen 의 The Innovation Solution 과 Jim Collins 의 How the Mighty Fall 에 잘 설명되고 있다.
3. 회사의 모바일 전략에 일관적인 전략이 부재하다.쉬미트회장과 고위임원들이 언급했듯이, 모바일은 구글 성장의 핵심이다. 초기의 모바일 매출이 성장궤도에 오르려면 상당한 시간이 필요할 것이다. 특히 구글의 모바일 광고회사 Admob 인수이후에 모바일시장에 규모있는 인수대상이 보이지 않는다. 대신, 최근의 ITA 인수는 중대규모의 투자를 통해 사업의 전개를 모색하는 일면을 보인다.
4. 결국, 사람, 사람, 사람에 관한 얘기다.구글의 엔지니어링 지배적인 문화는 우리에게 새로운 것이 아니다. 그러나 피터드러커가 기념비적인 저서 Innovation and Entrepreneurship 에서 언급했듯이, "성공적 혁신가는 사람을 본다". 구글은 너무 오래동안 특정 프로필의 사람들을 채용해왔다. 예를 들어, 프로덕트 매니저 지망생은 일류대학의 컴퓨터전공학위를 보유했어야 된다고 말했다. 구글의 핵심 알고리즘이 엔지니어링 혁신의 뛰어난 기능이었지만, 모두가 입을 모아 과연 그것이 지속되겠는가에 의문을 던진다. 붕어빵찍기와 같은 인사는 다양성과 비공학 전공자들의 한계 철폐 같은 중요한 기회를 상실하고 있으며 혁신을 저해하고 있다. 특히 짐 콜린스가 제기한 문화적 자만심은 가장 심대한 관심사다. 구글은 종종 엔지니어가 엔지니어링, 제품 그리고 심지어 마케팅 결정까지 리드하는 것으로 알려진다. 그러나 실패할때면, Google Wave 나 Google Radio 처럼, 비판은 구글이 정말 사람을 이해하고 있는지 묻는다.
이러한 이유외에도, 실리콘벨리에 "정통한" 관측자들이 현재 점점 더 묻게되는 질문은: 구글이 차기 마이크로소프트가 될 수 있는가? 이다. 이는 구글이 검색으로 혁명을 선도했듯이, MS가 시장지배적인 Window 와 MS Office 로 선구자였기 때문이다. 그러나 Xbox 이후에 새로운 혁신을 내놓는데 심각하게 갈등을 겪고있다. 보다 깊은 문화적 문제가 놀라운 성과와 성공에 가려져 있었다.
한가지 확실한 점은, 현재가 구글 역사상 중요한 시점이라는 점이다. 위에 언급한 문제들을 테이블에 올리지 않는다면, 비판은 증가할 것이다. 그러나 충분한 현금 보유력을 감안할때, 훌륭한 인재들과 커다란 난제를 접할 수 있다는 점에서, 이 순간을 기회로 본다. 이제는 반성할 기회다. 힘든 질문을 하면서, 도전을 공개적으로 토론하고, 신선한 인재와 생각들을 포용하여 이 글로벌 혁신의 위대한 심볼이 진화하고 성장하도록 해야 한다.
당신은 어떻게 생각하십니까? - 장수한다 아니면 단명이다. 과연 구글은 마이크로소프트 처럼 처할 위험에 있는걸까요 아니면 창조적 폭발 직전에 와 있는걸까요?
1. 구글은 과거 수년간 심각한 인재 유출을 겪었다.구글의 근속률은 높은 편이지만, 구글의 인재 문제는 수가 아니라 누가 나가며 왜 나가냐의 유형의 문제다. 구글의 인재 유출은 여기를 참조. Facebook 과 Zynga 는 실리콘벨리에서 가장 선호되는 직장으로 여겨지는데, 구글에서는 특히 중요시되는 모바일 관련 안드로이드 프로덕트 매니저인 Erick Tseng 과 같은 이가 Facebook 으로 줄줄이 떠나는 것을 보아왔다.구글 내부 소식에 가까운 이에 따르면, 구글 상부에 회사 초기의 혁신적 문화을 이끌던 관리자들이 천천히 교체되고 있다. 한정되어 있다고 느끼고 동기부여가 되지않는 기업가 타입과 석학들이 움직인다. 사람들은 심지어 2004-2005년간에 야후가 더이상 그들이 입사했던 이전의 실력주의가 통용되지 않아 사람들이 떠났던 일을 회상하게 한다고까지들 했다.
2. 회사는 이제 손쉽게 성장할 수 있는 기회가 바닥나고 큰 규모의 새로운 매출을 찾아야 한다.검색시장이 성장 한계에 다다른 만큼, "큰 투자"에 점점 더 필요성을 느낀다. 이것이 성숙단계에 접어든 회사의 CEO 가 "큰 숫자의 폭정"을 야기하는 문제다. 작은 기반에서 인상적으로 성장한 모바일 검색이 있지만, 회사의 근본적 차이를 만들기에는 아직 너무 작다. 회사는 분명히 미친듯이 모바일과는 다른 성장 동력을 찾으려 시도한다. 최근 7000억원 규모의 ITA 인수가 중간에서 대규모의 투자를 어떻게 전개할 것인가의 관점에서 좋은 사례가 된다. 이는 성장율을 유지하게 위해 점점 더 큰 부분의 매출을 찾아야 함이다. 이러한 문제는 혁신을 연구하는 학자인 Clayton Christensen 의 The Innovation Solution 과 Jim Collins 의 How the Mighty Fall 에 잘 설명되고 있다.
3. 회사의 모바일 전략에 일관적인 전략이 부재하다.쉬미트회장과 고위임원들이 언급했듯이, 모바일은 구글 성장의 핵심이다. 초기의 모바일 매출이 성장궤도에 오르려면 상당한 시간이 필요할 것이다. 특히 구글의 모바일 광고회사 Admob 인수이후에 모바일시장에 규모있는 인수대상이 보이지 않는다. 대신, 최근의 ITA 인수는 중대규모의 투자를 통해 사업의 전개를 모색하는 일면을 보인다.
4. 결국, 사람, 사람, 사람에 관한 얘기다.구글의 엔지니어링 지배적인 문화는 우리에게 새로운 것이 아니다. 그러나 피터드러커가 기념비적인 저서 Innovation and Entrepreneurship 에서 언급했듯이, "성공적 혁신가는 사람을 본다". 구글은 너무 오래동안 특정 프로필의 사람들을 채용해왔다. 예를 들어, 프로덕트 매니저 지망생은 일류대학의 컴퓨터전공학위를 보유했어야 된다고 말했다. 구글의 핵심 알고리즘이 엔지니어링 혁신의 뛰어난 기능이었지만, 모두가 입을 모아 과연 그것이 지속되겠는가에 의문을 던진다. 붕어빵찍기와 같은 인사는 다양성과 비공학 전공자들의 한계 철폐 같은 중요한 기회를 상실하고 있으며 혁신을 저해하고 있다. 특히 짐 콜린스가 제기한 문화적 자만심은 가장 심대한 관심사다. 구글은 종종 엔지니어가 엔지니어링, 제품 그리고 심지어 마케팅 결정까지 리드하는 것으로 알려진다. 그러나 실패할때면, Google Wave 나 Google Radio 처럼, 비판은 구글이 정말 사람을 이해하고 있는지 묻는다.
이러한 이유외에도, 실리콘벨리에 "정통한" 관측자들이 현재 점점 더 묻게되는 질문은: 구글이 차기 마이크로소프트가 될 수 있는가? 이다. 이는 구글이 검색으로 혁명을 선도했듯이, MS가 시장지배적인 Window 와 MS Office 로 선구자였기 때문이다. 그러나 Xbox 이후에 새로운 혁신을 내놓는데 심각하게 갈등을 겪고있다. 보다 깊은 문화적 문제가 놀라운 성과와 성공에 가려져 있었다.
한가지 확실한 점은, 현재가 구글 역사상 중요한 시점이라는 점이다. 위에 언급한 문제들을 테이블에 올리지 않는다면, 비판은 증가할 것이다. 그러나 충분한 현금 보유력을 감안할때, 훌륭한 인재들과 커다란 난제를 접할 수 있다는 점에서, 이 순간을 기회로 본다. 이제는 반성할 기회다. 힘든 질문을 하면서, 도전을 공개적으로 토론하고, 신선한 인재와 생각들을 포용하여 이 글로벌 혁신의 위대한 심볼이 진화하고 성장하도록 해야 한다.
당신은 어떻게 생각하십니까? - 장수한다 아니면 단명이다. 과연 구글은 마이크로소프트 처럼 처할 위험에 있는걸까요 아니면 창조적 폭발 직전에 와 있는걸까요?
Essay on IBM Service Science
Recently, I came across a my short old article on IBM Service Science which I contributed to Korean Journal of Technology Management in 2007. A number of Universities including UC Berkeley, North Carolina State University and Sogang University offers a major in Service Science now a days. From Industry Associations, Korea Society of IT Services and Service Science Network Forum are also active on this research in Korea society. If you're interested in IBM Service Science, I encourage you to visit here.
Short Korean article on lead user innovation
I contributed an article on lead user innovation to the monthly Journal of Marketing in Korea probably one and half year ago. Title was lead user innovation in the context of open innovation. Open innovation and lead user innovation has been often used interchangably but certainly these two areas are distinct in some point, and professor, Joel West in Sanjose University maintains this aspect. I strived to view the lead user innovation from the perspective of product innvation point and stresssed that lead user innvation would be an intriguing research subject from the juction of marketing and product innovation.
How Big Companies can stop the brain drain
From Fortune Magazine
Across all industries, the best and brightest are striking out on their own to escape corporate bureaucracy. That need not be the case. Here's how big institutions can re-imagine themselves as centers of innovation.
By John Hagel III and John Seely Brown
People are increasingly pursuing the jobs and endeavors for which they have the most passion. It is not a surprise then that many of the most passionate and talented individuals are leaving their corporate homes and striking out on their own.
Passionate individuals are fleeing the institutional environs that constrain, rather than amplify, individual passion and creativity. They can no longer abide being a passive cog in a highly scripted and often stultifying corporate machine.
But the flight from big institutions will be a temporary, transitional phenomenon if those institutions are able to reimagine how they organize themselves and conduct their operations. Once they do, they'll become a natural home for passionate individuals. Here's how they'll do it.
The challenge for institutional leaders in the near term is to find and motivate talented individuals to engage in the task of transforming institutions rather than fleeing them. To attract these passionate individuals, leaders first have to identify them. The Silicon Valley entrepreneur Tara Lemmey has a useful way to identify questing, passionate individuals. In general, she's looking for people who can thrive in different kinds of cultural environments and cross-pollinate ideas and practices among them.
To find out whether an individual has these qualities, Tara takes a job candidate out to lunch, and then, once the food arrives, offers to share a bite of hers. "People who won't share food don't do well with us," says Lemmey. "It's a brutal indicator. People who share food tend to be less territorial. They're more likely to say, 'Hey, what's the table ordering? I want to try a little of everything.' Those folks tend to have a lot more ease in our working process."
To attract these kinds of people, leaders should articulate a new rationale for the firm that can appeal directly to the passionate and offer them the promise of more rapid development of their talents. If companies take talent development seriously, they begin to realize that, in the words of Silicon Valley icon Bill Joy, "There are always more smart people outside your company than within it." If firms are serious about developing their talent, they must find more ways to connect and collaborate with all of those smart people outside the organization. Even more important, they should aggressively create opportunities for people within the organization to work with leading-edge talent outside it.
2) Be a leader on growth
Institutional leaders must resist the instinctive tendency when under pressure to batten down the hatches and assume a defensive posture, the better to protect the core that generates the cash. Instead, the leaders of today's big corporate institutions must begin to pursue major new sources of growth.
Talent thrives when it has new challenges and opportunities to pursue. Institutions that are on the defensive with low-growth strategies simply cannot offer the same level of talent development to their employees. When such institutions are at their worst, a vicious cycle takes hold. As the firm goes on the defensive, the most creative talent becomes more vulnerable to offers from higher-growth firms. Performance deteriorates further as talent flees, and finally, the institution settles into its defensive posture and another wave of the talent exodus begins.
This is where leadership is desperately needed. Institutional leaders must provide compelling motivation for people in the core of the business to venture out to relevant edges—whether those edges are geographic, demographic, or between companies—in search of major new growth opportunities. This means putting a premium on strategies that move beyond straight-line growth within the core and that motivate investment in new growth options. Such a shift in strategic focus will inexorably pull the organization toward promising edges where growth potential is the highest—indeed, that's virtually the only place where major new growth options can be found.
3) Leverage your risk takers
Redefining the rationale of the firm will begin to attract a critical mass of passionate individuals from all parts of the company, but especially from the periphery, where many of the people with the greatest passion tend to congregate. These areas tend to attract risk-takers, people who seek out new challenges and opportunities to drive their own performance to new levels, people who are not only more passionate than those at the core but who tend to have new approaches, practices, and dispositions.
Here's how to find these risk-takers, while at the same time leveraging the strengths that big organizations offer:
Pull people out of the core. Questing explorers are likely to be in short supply. That's why institutional leaders must find ways to motivate the more risk-averse employees in the core of the business—who are likely to be the vast majority of employees— to venture out and connect with their more passionate, questioning colleagues on the edge. These questing explorers need access to the core of the firm and the ability to mobilize their colleagues so that they can scale the emerging growth opportunities that they tend to see and embrace first.
Provide leverage through focused initiatives. As groups of questing individuals coalesce both within and across the boundaries of the firm, they can begin to launch low-risk, high-reward initiatives. Rather than seeking the journey's end in one massive bound, it's best for these groups to recognize that a journey of a thousand miles begins with a single step, followed by another, and another. Starting slowly, below the radar, gives the champions of change opportunities to have small successes and gain strength while gradually neutralizing the inevitable resistance of entrenched interests.
Provide leverage through pull platforms. One of the most powerful ways to drive leveraged growth is to design and deploy scalable pull platforms that reach well beyond the boundaries of the firm to access and attract relevant talent wherever it resides. Rather than trying to specify the activities in processes in great detail, orchestrators of pull platforms specify what they want to come out of the process, providing more space for individual participants to experiment, improvise, and innovate. This kind of modularity—in which the outputs are specified but not the inputs— is powerfully motivating for passionate individuals. In a similar way, instead of dictating precisely how to do their jobs, legendary coach and general manager Al Davis of the Oakland Raiders used to tell football players: "Just win, baby." That's also good advice for anyone in business today.
-- John Hagel III, co-chairman, and John Seely Brown, independent co-chairman, of the Deloitte Center for the Edge, have a passion for communicating world-changing ideas in ways that get executives to change what they do and realize significant performance benefits. Their books include The Power of Pull, The Only Sustainable Edge, Out of the Box, Net Worth, and Net Gain.
2010년 11월 12일 금요일
Open Service Innovation web cast
Open Service Innovation
Henry Chesbrough, world-renown scholar who coined the term open innovation unveiled the idea of his next book “open service innovation” at the opensource.com webcast sponsored by Red Hat community service together with one of management guru, Gary Hamel. I particularly like these two scholars because of their creative but also inspiring perspective stems from the industry experiences at the trenches.
Henry mentioned about the commodity trap from the examples of Motorola and then Nokia.
Henry Chesbrough, world-renown scholar who coined the term open innovation unveiled the idea of his next book “open service innovation” at the opensource.com webcast sponsored by Red Hat community service together with one of management guru, Gary Hamel. I particularly like these two scholars because of their creative but also inspiring perspective stems from the industry experiences at the trenches.
Henry mentioned about the commodity trap from the examples of Motorola and then Nokia.
He articulated the Porter’s value chain and explained that Porter’s value chain which put the services at the tail of the chain was wrong. He claimed that service should be placed at the center of value chain to differentiate the competitive landscape, and perhaps by devising the different business model towards more lucrative businesses.

First thing come to my mind at this moment was, innovator dilemma expressed from Clayton M. Christensen. Great company focused on relationship with current customer, hence often to neglect the disruptive technology or innovation. Motorola and Nokia focused on operational excellence to compete against market share, whereas Google and Apple crafted the strategic positioning through the shaping of platform based service business model.
Henry described the so-called a “service value web”, in which customer experiences were centered around the cycles of value activities.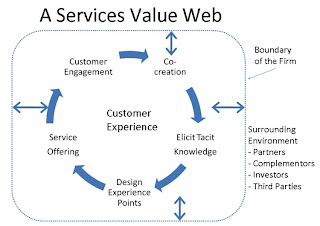
He also exampled the case where service view of transportation has unlocking the hidden business value. If transportation was viewed as service from the inception, untapped large amount of parts became a source of value. Henry attempted to explain this differentiated value proposition by illustrating the term as “utilization differential”.
Argument here is, how can you sustain differentiation in services? The answer is, service platform. Service platform can sustain the differentiation. Certainly iPhone and Android would be a great manifestation of this. Henry showed the UPS, Amazon, and TSMC foundry Semi conductor business as a examples of service platforms.
My impression? This is nothing new to me. But I think this is natural consequences after the open business model debut if we take into account the rising tide of iPhone and SW service or networked business model. All of these stems from the flourish of external network effect and increasing return cycle of effect in ICT environment. Given the consideration that Henry’s main researches are Open Innovation, Open Business Model and Service Science, it is expected to augment to these service area, and in fact, it is timely and smart approaches to augment the research into the platform based service spaces.
Henry described the so-called a “service value web”, in which customer experiences were centered around the cycles of value activities.

He also exampled the case where service view of transportation has unlocking the hidden business value. If transportation was viewed as service from the inception, untapped large amount of parts became a source of value. Henry attempted to explain this differentiated value proposition by illustrating the term as “utilization differential”.
Argument here is, how can you sustain differentiation in services? The answer is, service platform. Service platform can sustain the differentiation. Certainly iPhone and Android would be a great manifestation of this. Henry showed the UPS, Amazon, and TSMC foundry Semi conductor business as a examples of service platforms.
My impression? This is nothing new to me. But I think this is natural consequences after the open business model debut if we take into account the rising tide of iPhone and SW service or networked business model. All of these stems from the flourish of external network effect and increasing return cycle of effect in ICT environment. Given the consideration that Henry’s main researches are Open Innovation, Open Business Model and Service Science, it is expected to augment to these service area, and in fact, it is timely and smart approaches to augment the research into the platform based service spaces.
If you want to see this webcast, please visit here to watch the 1 hour presentation with Q&A from Henry Chesbrough and Gary Hamel. But I think you are required to register to join this webcast.
피드 구독하기:
덧글 (Atom)
